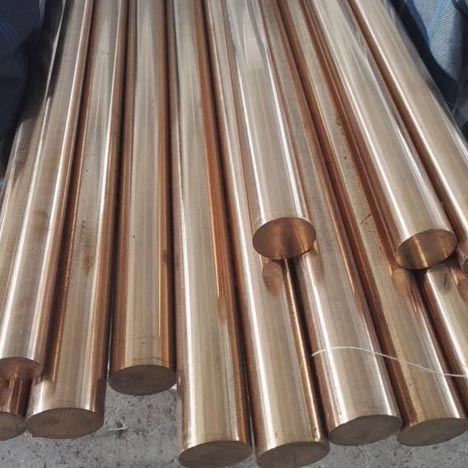
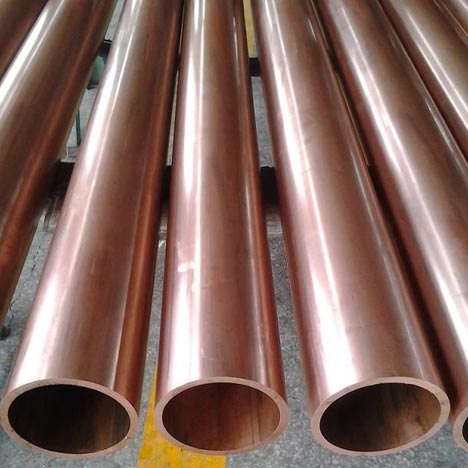







Red Copper Series
Red copper is industrial pure copper. Because of its rose red, the surface of the oxide film is purple, so it is generally called red copper, also known as red copper. It is copper containing a certain amount of oxygen, so it is also called oxygen-containing copper, and sometimes can be regarded as copper alloy.
Copper gets its name from its purplish red color. It is not necessarily pure copper, sometimes a small amount of deoxidization or other elements are added to improve the material and performance
Email: [email protected]
WhatsApp: 0086-18301953841

| Grade list of copper and copper alloys by country | |||||||
| Classification | China | Germany | America | Japan | England | Europe | International |
| oxygen free copper | TU1 | 2.0076 | C10200 | C1020R | C103 | ||
| TU2 | Cu-OF-H110 | C11000 | c1011 | C101 | |||
| Vacuum oxygen free copper | E-Cu58 | TU00 | c1020 | 6N | |||
| high purity | copper-OFE | c10500 | c10700 | ||||
| Silver copper | TAg 0.1 | CuAg 0.1 | C10400 | C1040 | CuAg 0.1 | ||
| brass | H90 | CuZn10 | C22000 | C2200 | CZ101 | CuZn10 | CW501L |
| H70 | CuZn30 | C26000 | C2600 | CZ106 | CuZn30 | CW505L | |
| H68 | C26200 | C2620 | CuZn33 | CW506L | |||
| H65 | CuZn35 | C27000 | C2700 | CZ107 | CuZn36 | CW507L | |
| H63 | CuZn37 | C27200 | C2720 | CZ108 | CuZn37 | CW508L | |
| H62 | CuZn40 | C28000 | C2800 | CZ109 | CW509L | ||
| bronze | QSn4-0.3 | CuSn4 | C51100 | C5111 | PB101 | CuSn4 | CW450K |
| CuSn5 | C51000 | C5101 | CuSn5 | CW451K | |||
| QSn6.5-0.1 | CuSn6 | C51900 | C5191 | PB103 | CuSn6 | CW452K | |
| QSn8-0.3 | CuSn8 | C52100 | C5210 | CuSn8 | CW453K | ||
| QSn6.5-0.4 | |||||||
| copper-nickel | BZn18-18 | CuNi18Zn20 | C75200 | C7521 | NS106 | CuNi18Zn20 | |
| BZn18-26 | CuNi18Zn27 | C77000 | C7701 | NS107 | CuNi18Zn27 | CW410J | |
| BZn15-20 | C7541 | CW409J | |||||
| BZn18-10 | C7350 | ||||||
| pure copper | TU2 | OF-Cu58 | C10100 | C1011 | C101 | CW008A | copper oxide |
| T2 | SW——copper | C11000 | C1100 | C101 | copper - FRHC | ||
| TP2 | SF-Cu | C12200 | C1220 | C106 | CW024A | copper - DHP | |
| TP1 | SW-copper | C12000 | C1201 | CW023A | copper DLP | ||
Ordinary performance
Red copper is a kind of pure copper, generally can be approximately considered as pure copper, conductivity, plasticity are better, but the strength, hardness is poor. Copper has excellent thermal conductivity, ductility and corrosion resistance. Trace impurities in copper have a serious effect on the conductivity and thermal conductivity of copper. Among them, titanium, phosphorus, iron and silicon significantly reduce the conductivity, while cadmium and zinc have little effect. The solubility of sulfur, selenium and tellurium in copper is very small, and they can form brittle compounds with copper, which have little effect on electrical conductivity, but can reduce the plasticity of processing.
Copper in the atmosphere, sea water and some non-oxidizing acid (hydrochloric acid, dilute sulfuric acid), alkali, salt solution and a variety of organic acids (acetic acid, citric acid), has good corrosion resistance, used in the chemical industry. In addition, copper has good weldability, can be cold, thermoplastic processing into a variety of semi-finished products and finished products. In the 1970s, the production of red copper exceeded the total production of all other copper alloys.
Physical properties
Trace impurities in copper have a serious effect on the conductivity and thermal conductivity of copper. Among them, titanium, phosphorus, iron and silicon significantly reduce the conductivity, while cadmium and zinc have little effect. The solubility of oxygen, sulfur, selenium and tellurium in copper is very small, and can form brittle compounds with copper, which has little effect on electrical conductivity, but can reduce the plasticity of processing. When ordinary red copper is heated in a reducing atmosphere containing hydrogen or carbon monoxide, hydrogen or carbon monoxide is easy to interact with cuprous oxide (Cu2O) on the grain boundary to produce high-pressure water vapor or carbon dioxide gas, which can rupture copper. This phenomenon is often called the "hydrogen disease" of copper. Oxygen is harmful to the weldability of copper. Bismuth or lead and copper produce eutectic with low melting point, which makes copper produce hot embritleability. When the brittle bismuth is distributed in thin films along grain boundaries, the copper becomes cold brittle. Phosphorus can significantly reduce the electrical conductivity of copper, but can improve the fluidity of copper liquid, improve weldability. Appropriate amount of lead, tellurium, sulfur, etc. can improve the machinability. The tensile strength of the annealed copper sheet at room temperature is 22 ~ 25 kg force/mm 2, the elongation is 45 ~ 50%, and the Brinell hardness (HB) is 35 ~ 45.
1. Oxyacetylene Welding
Copper oxygen acetylene welding can be used wire 201 (or wire 202) wire and flux 301. After 400~700℃ preheating before welding, welding flame using neutral flame and larger flame power. With fewer welding layers, the welding stress is reduced by hammering after welding.
2. Shielded Metal Arc Welding
Copper electrode arc welding can choose copper 107 or copper 227 electrode. The power supply is reversed dc connection. The preheating temperature before welding is 300~500℃. Short arc and straight line are used during welding. After welding, the welding seam is hammered to reduce the welding stress.
3. Argon Tungsten-arc Welding
The welding wire and flux used in copper tungsten arc welding are the same as that used in oxyacetylene welding, and the power supply is directly connected with dc. Preheat before welding, but the temperature should not be too high.
Red copper is used much more widely than pure iron, and every year 50% of the copper is purified by electrolysis for use in the electrical industry. The copper mentioned here should be very pure indeed, and contain more than 99.95% copper. A very small amount of impurities, especially phosphorus, arsenic, aluminum, etc., will greatly reduce the conductivity of copper. It is mainly used for making electric equipment such as generator, bus, cable, switching device, transformer and heat conduction equipment such as heat exchanger, pipe, flat collector of solar heating device. Oxygen in copper (copper smelting is easy to mix with a small amount of oxygen) has a great impact on conductivity, used for electrical industry copper generally must be oxygen-free copper. In addition, lead, antimony, bismuth and other impurities will make the crystallization of copper can not be combined together, resulting in hot brittleness, will also affect the processing of pure copper. This kind of pure copper with high purity is generally refined by electrolysis: the impure copper (coarse copper) is used as anode, the pure copper is used as cathode, and the copper sulfate solution is used as electrolyte. When the current passes through, the impure copper on the anode gradually melts, and the pure copper gradually precipitates on the cathode. The copper thus refined. Purity up to 99.99%.
Copper is also used in motor short circuit ring, electromagnetic heating sensor production and high power electronic components, wiring bar terminals and so on.
Copper is also used in doors, Windows, handrails and other furniture and decoration.
We also provide CNC precision machining services for our clients, covering industries such as energy, petrochemicals, steel, engineering machinery, plastics, prevention and control, hydraulics, healthcare, and food. Please feel free to send us drawings for inquiries.









